What were the consequences of the Vietnam War?
Topic of Study [For H2 History Students]:
Paper 1: Understanding the Cold War (1945-1991)
Section A: Source-based Case Study
Theme I Chapter 2: A World Divided by the Cold War – Manifestations of the global Cold War: Vietnam War (1955-75)
Topic of Study [For H1 History Students]:
Essay Questions
Theme II Chapter 2: The Cold War and Southeast Asia (1945-1991): The Second Indochina War (1964-1975)
Contextual Analysis
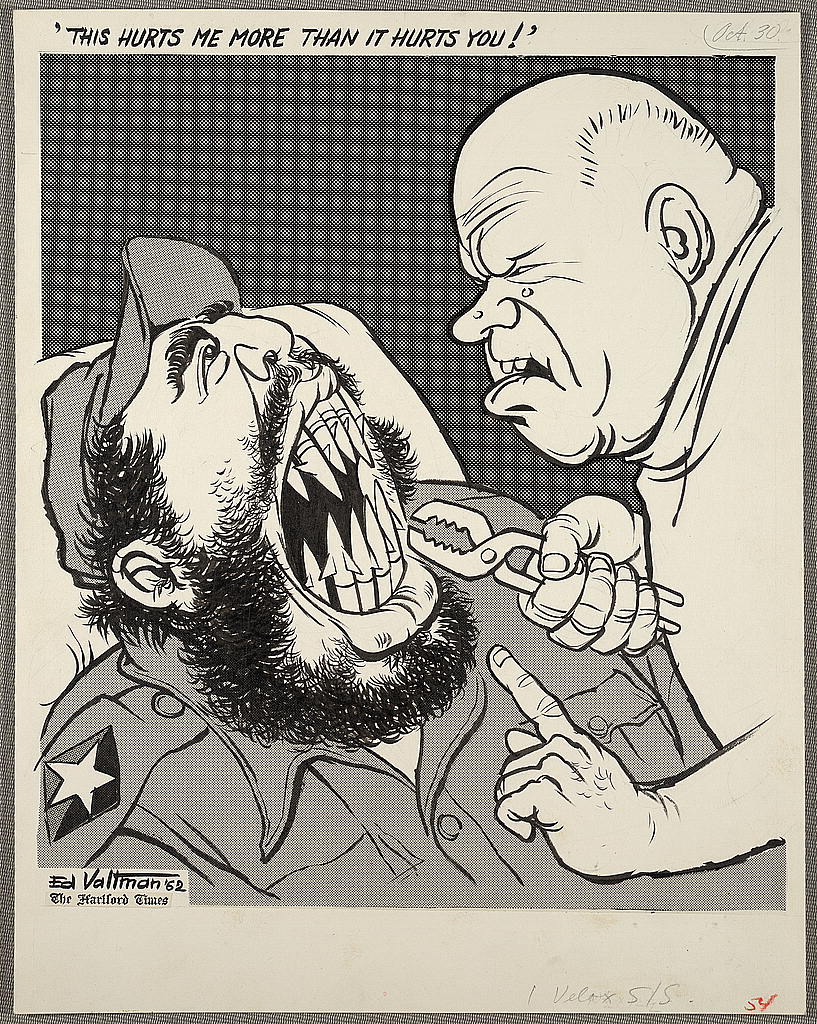
In the previous article, we have examined the historical developments of the first and second Indochina Wars. Next, it is imperative to consider the political impacts of the Vietnam War on the superpowers – USA and Soviet Union.
1. Impacts on the USA: ‘Vietnam Syndrome’
Notably, the withdrawal of USA from Vietnam was largely influenced by anti-war sentiments. Many young Americans were against the drafting process. Also, the growing disillusionment and exposed war atrocities (especially the ‘My Lai massacre’) created the impetus for citizens to demand the immediate withdrawal.
Furthermore, critics questioned the necessity of US involvement in the politics of other countries even though many still supported the notion of ‘defending democracy’. As these doubts surfaced, some argued that US Presidents should not be given extensive powers to wage wars without Congress approval.
1.1. The War Powers Act
In November 1973, the War Powers Act (also known as the ‘War Powers Resolution’) was passed as a congressional resolution to curtail the US President’s ability to conduct foreign military campaigns. Its main purpose was to prevent US from being trapped in costly and protracted wars, like the conflict in Vietnam.
This Act required the president to seek congressional approval before American troops can be deployed overseas. For instance, the President has to inform the Congress within 48 hours.
Although President Nixon vetoed the law by claiming that it was ‘unconstitutional and dangerous’, the Congress overrode his action.
However, the congressional resolution proved futile as future US Presidents found ways and means to circumvent it. For example, President Ronald Reagan deployed troops in El Salvador in the 1981, during the renewed confrontation with the Soviets.
1.2. The Detente
As the world was on the brink of nuclear confrontation in the late 1960s due to the Sino-Soviet split, USA changed its diplomatic stance towards China. Additionally, in the early 1970s, the Nixon administration extended an ‘olive branch’ to Soviet Union in the form of diplomatic visits.
On 22 May 1972, Nixon visited his Cold War rival, Leonid Brezhnev in Moscow. It marked the first-ever visit by an American president to Soviet Union. The key takeaway from these visits was the increased mutual cooperation.
For example, the Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT I) Agreement was signed on 26 May 1972. The Agreement signified the mutual decisions of the superpowers to halt the build-up of strategic ballistic missile launchers. The SALT II Treaty was signed later in the 1970s that banned the development of new ballistic missiles for both countries.
Also, this phase of the Cold War led to the push for space exploration. In July 1975, both USA and USSR conducted a joint-space flight and encouraged collaboration.
However, the thawing of superpower relations halted when Soviet Union invaded Afghanistan in December 1979. Tensions resurfaced as USA boycotted the 1980 Summer Olympics in Moscow.
2. Impacts on the USSR: Race in the Third World
On the other hand, the Second Indochina War prompted the Soviet government to intensify its efforts to support the Communist regime. Ho Chi Minh’s victory in Indochina was hailed as a significant victory against the Americans.
As such, Soviet Union raised its military expenditures to support its Cold War allies. As stated earlier, its campaign in the Third World regions began with the invasion in Afghanistan. This conflict was a turning point as observers noted that Soviet Union invaded a country outside the Eastern Bloc, such that its actions drew international criticisms.
The Soviet occupation of Afghanistan was carried out with the intention to reinforce the Brezhnev Doctrine, in which the government seems to secure its political influence in these socialist countries.
However, the campaign in Afghanistan proved disastrous for Soviet Union. The protracted conflict was perceived by some historians as “Soviet Union’s Vietnam War”, particularly due to the mounting economic costs.
What can we learn from this article?
Consider the following question:
– Assess the political significance of the Second Indochina War on the USA [to be discussed in class].
Besides the topical review of this Cold War event, it is important that you attempt source-based case study questions or essay questions to determine whether you have fully understood these historical developments. Join our JC History Tuition and get additional support as we provide numerous practice questions and answer outlines. By doing so, we ensure that you can study productively and effectively to perform well for the GCE A Level History examinations.
The H2 and H1 History Tuition feature online discussion and writing practices to enhance your knowledge application skills. Get useful study notes and clarify your doubts on the subject with the tutor. You can also follow our Telegram Channel to get useful updates.
We have other JC tuition classes, such as JC Math Tuition and JC Chemistry Tuition. For Secondary Tuition, we provide Secondary English Tuition, Secondary Math tuition, Secondary Chemistry Tuition, Social Studies Tuition, Geography, History Tuition and Secondary Economics Tuition. For Primary Tuition, we have Primary English, Math and Science Tuition. Call 9658 5789 to find out more.