What happened in the Hungarian uprising?
Topic of Study [For H2 History Students]:
Paper 1: Safeguarding International Peace and Security
Section B: Essay Writing
Theme III Chapter 2: Political Effectiveness of the UN in maintaining international peace and security
Historical Context: De-Stalinisation
On 25 February 1956, Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev delivered a secret speech titled ‘On the Cult of Personality and its Consequences’. Khrushchev denounced Stalin’s style of leadership, which proved shocking to many Soviet officials.
Comrades, we must abolish the cult of the individual decisively, once and for all; we must draw the proper conclusions concerning both ideological-theoretical and practical work.
…Secondly, to continue systematically and consistently the work done by the party’s central committee during the last years… characterized by the wide practice of criticism and self-criticism.
An excerpt from Khrushchev’s Secret Speech, 25 Febrary 1956.
In response to the surprising development barely three years after Stalin’s death, thousands of protestors gathered at the streets on 23 October, demanding democratisation. Initially, the protests appeared to have succeeded.
The Soviet Response
Hungarian politician Imre Nagy became Prime Minister. As the face of the Hungarian Revolution, Nagy called for the withdrawal of Soviet forces from Hungary and promised democratic reforms. However, Nagy’s unilateral withdrawal of Hungary from the Warsaw Pact proved disastrous.
On 4 November 1956, the Soviet Union conducted a military invasion of Hungary. Nagy was tried and executed two years later. The violent confrontation led to growing questions by Western observers on the extent of Soviet control in Eastern Europe, in spite of Khrushchev’s de-Stalinisation that pledged the end of a repressive rule.
The United Nations: Too little, too late?
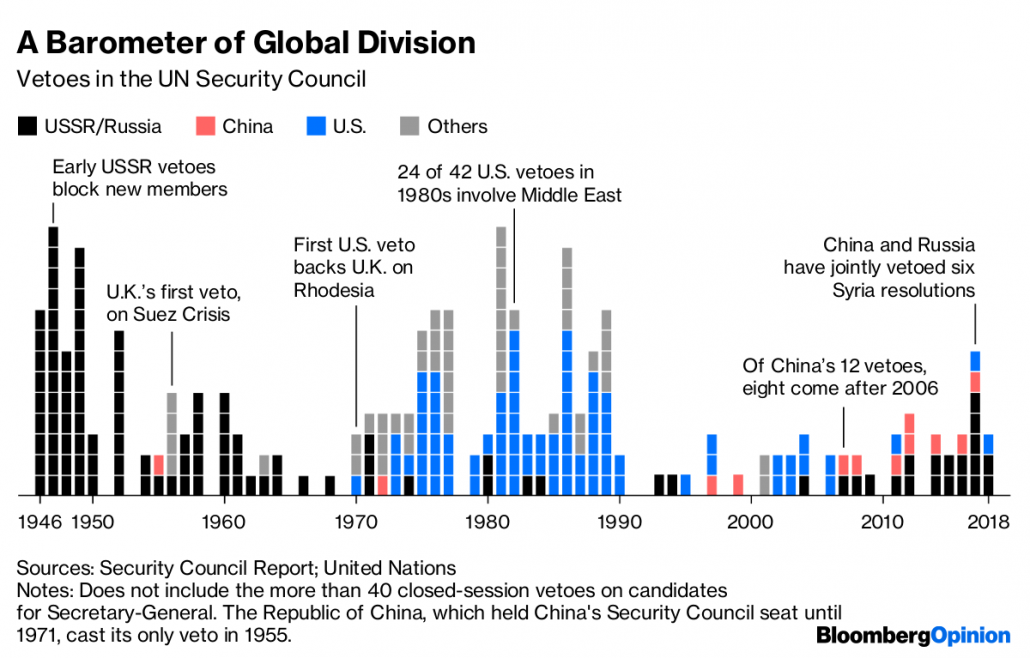
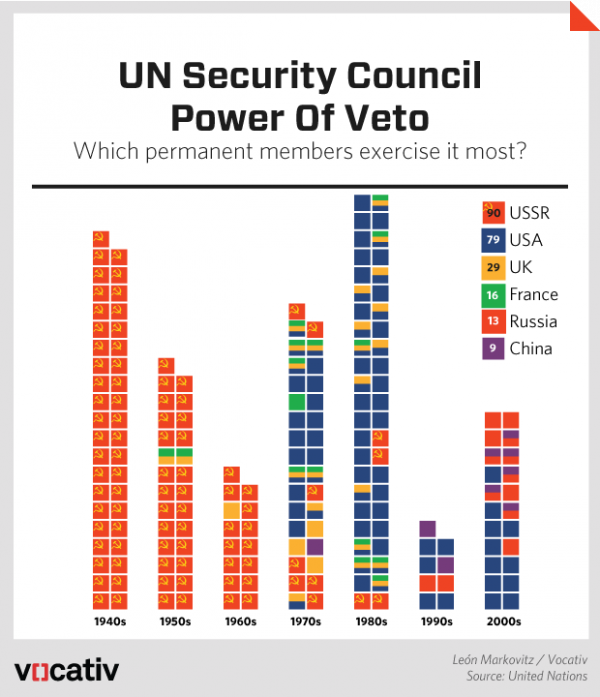
The United Nations Security Council adopted Resolution 120, considering the grave situation created by the USSR in suppression the Hungarian people. However, Soviet Union vetoed. Although the Security Council managed to invoke the ‘Uniting for Peace’ Resolution [UNGA Resolution 377A(V)] to call for an emergency special session, the United Nations was unable to conduct an investigation on the political situation in Hungary.
The Soviet Union suppressed the Hungarian uprising in the fall of 1956 and executed Imre Nagy, the government’s reformist leader. World public opinion was just as aroused by Hungary as Suez. The General Assembly condemned the Soviet Union, but the Soviet Union ignored the condemnation. Hammarskjöld came up with no dramatic gestures to put himself into the conflict. At the height of the Cold War, the U.N. was powerless to bend any of the two superpowers to its will.
An excerpt from “United Nations: A History” by Stanley Meisler.
What can we learn from this article?
Consider the following question:
– How far do you agree that Soviet Union obstructed the functions of the United Nations during the Cold War?
Join our JC History Tuition and learn more about the United Nations. The H2 and H1 History Tuition feature online discussion and writing practices to enhance your knowledge application skills. Get useful study notes and clarify your doubts on the subject with the tutor. You can also follow our Telegram Channel to get useful updates.
We have other JC tuition classes, such as JC Math Tuition and JC Chemistry Tuition. For Secondary Tuition, we provide Secondary English Tuition, Secondary Math tuition, Secondary Chemistry Tuition, Social Studies Tuition, Geography, History Tuition and Secondary Economics Tuition. For Primary Tuition, we have Primary English, Math and Science Tuition. Call 9658 5789 to find out more.