What happened during the Taiwan Straits Crises?
Topic of Study [For H1 History Students]:
Section B: Essay Writing
Theme II: Cold War in Asia [1945-1991] – Superpower relations with China (1950-1979)
The First Taiwan Straits Crisis: A geopolitical contest
Following the Chinese Communist Party’s (CCP) victory over the Kuomintang (KMT) during the Chinese Civil War in 1949, the latter fled to Taiwan. The Taiwan Strait separated mainland China from Taiwan as the KMT formed the Republic of China (ROC).
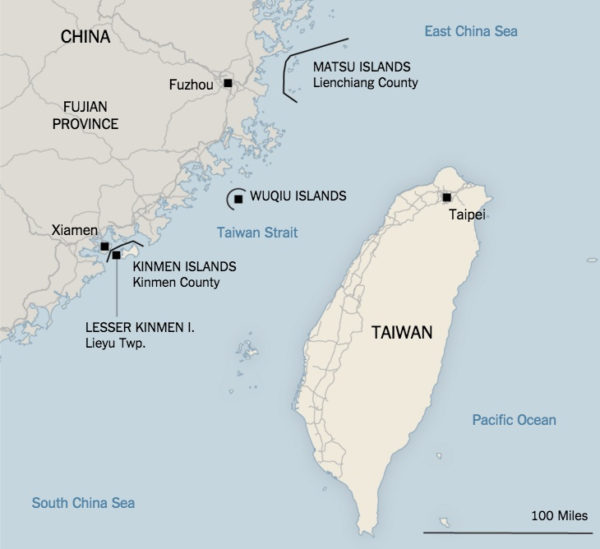
Quemoy (金门 or Kinmen) and Matsu (马祖) Islands were considered the first line of defence for Chiang Kai-shek’s ROC. Additionally, the United States offered to aid its newfound ally, the ROC, especially after its hostile interactions with Chinese troops during the Korean War.
Notably, US President Harry Truman delivered a rousing speech that reaffirmed the American commitment to its political alliances in East Asia, including Taiwan.
Accordingly I have ordered the 7th Fleet to prevent any attack on Formosa. As a corollary of this action I am calling upon the Chinese Government on Formosa to cease all air and sea operations against the mainland. The 7th Fleet will see that this is done. The determination of the future status of Formosa must await the restoration of security in the Pacific, a peace settlement with Japan, or consideration by the United Nations.
An excerpt from a statement by the US President Harry Truman on Korea, 27 June 1950.
A Mutual Defense Treaty was signed with ROC to legitimise American military presence in the vicinity. Yet, such actions proved aggravating to Sino-American relations. In early September 1954, the PRC launched the bombardment of Quemoy and Matsu Islands. Chiang deployed about 100,000 troops to defend the two outermost islands, hoping that the American allies would come to their aid.
After the first crisis, the US Congress passed the “Formosa Resolution” that granted President Eisenhower the authority to defend Taiwan from communist aggression.
The Second Taiwan Straits Crisis: The Conflagration
During the Bandung Conference of 1955, Chinese Premier Zhou Enlai expressed desire to negotiate with the United States, possibly to de-escalate tensions and avert a full-scale military conflict with it. The olive branch offered by Zhou to the United States had earned much support and praise from the attendees at the Asian-African Conference in Indonesia.
By following the principles of mutual respect for sovereignty and territorial integrity, nonaggression, non-interference in each other’s internal affairs, equality and mutual benefit, the peaceful coexistence of countries with different social systems can be realized. When these principles are ensured of implementation, there is no reason why international disputes cannot be settled through negotiation.
An excerpt from Premier Zhou Enlai’s speech during the Asian-African Conference, 19 April 1955.
However, efforts to reduce tensions were negated by Eisenhower’s contemplated to use nuclear weapons on the PRC. On 23 August 1958, the Chinese leader Mao Zedong authorised the artillery bombardment of Quemoy Island. In retaliation, the ROC armed forces fought back.
Under the obligations of the American-Taiwan defense treaty of 1954, the United States offered military aid to the Nationalists. Increased American presence in the Taiwan Straits had alarmed the Soviet Union, such that Foreign Minister Andrei Gromyko visited Beijing to uncover the rationale behind Mao’s decision to attack Quemoy. Fortunately, the conflict did not escalate into a nuclear confrontation.
Chairman Mao said that the bombardment of Jinmen, frankly speaking, was our turn to create international tension for a purpose. We intended to teach the Americans a lesson. America had bullied us for many years, so now that we had a chance, why not give it a hard time?
… In our propaganda, however, we still need to condemn the Americans for causing tension in the Taiwan Straits. We did not put them in the wrong. The United States has several thousand troops stationed on Taiwan, plus two air force bases there. Their largest fleet, the Seventh Fleet, often cruises in the Taiwan Straits.
An excerpt from the “Inside Story of the Decision Making during the Shelling Jinmen” by Wu Lengxi
A thorn in the flesh: Prelude to the Sino-Soviet Split
On 6 October 1958, a ceasefire was made. Yet, the peace was short-lived as the PRC resumed its attacks on the two islands for nearly two decades until the late 1970s due to the Sino-American rapprochement.
Along the same vein, the Taiwan Straits Crises in the 1950s had impacted Sino-Soviet relations. On the surface, it appeared as if the signing of the Treaty of Friendship had proved to be fortuitous for Mao Zedong as he received Soviet military support to deter American attacks. Yet, the diverging perceptions by the two Communist leaders began to cause the gradual deterioration of bilateral relations. Partly, Khrushchev’s hesitance to antagonise the United States could be traced to his notion of “Peaceful Coexistence” that Mao could not agree with.
New evidence suggests that, on the contrary, the Soviet Union did everything it had promised to do in support of the Chinese operation, and that it was China, not the USSR, that was unwilling to follow through. This outcome explains why Khrushchev, feeling he had been burned once, was determined not to let it happen again. From then on he emphasized the need for a peaceful resolution of the Taiwan problem, a lesson that Mao was unwilling to draw, for fear it would expose the magnitude of his failure in the Quemoy crisis. These different views became a sore point in Sino-Soviet relations, as was evident during Khrushchev’s visit to Beijing in the autumn of 1959.
An excerpt from “The USSR Foreign Ministry’s appraisal of Sino-Soviet relations on the eve of the Split, September 1959” by Mark Kramer.
What can we learn from this article?
Consider the following question:
– Assess the view that the Taiwan conflict was the root cause of the Sino-Soviet split.
Join our JC History Tuition to analyse the significance of Taiwan and other related factors that shaped superpower relation with China. The H2 and H1 History Tuition feature online discussion and writing practices to enhance your knowledge application skills. Get useful study notes and clarify your doubts on the subject with the tutor. You can also follow our Telegram Channel to get useful updates.
We have other JC tuition classes, such as JC Math Tuition and JC Chemistry Tuition. For Secondary Tuition, we provide Secondary English Tuition, Secondary Math tuition, Secondary Chemistry Tuition, Social Studies Tuition, Geography, History Tuition and Secondary Economics Tuition. For Primary Tuition, we have Primary English, Math and Science Tuition. Call 9658 5789 to find out more.











