How did the UN respond to the Suez Canal crisis?
Topic of Study [For H1/H2 History Students]:
Paper 1: Safeguarding International Peace and Security
Section B: Essay Writing
Theme III Chapter 2: Political Effectiveness of the UN in maintaining international peace and security
Historical Context: Trouble in Suez
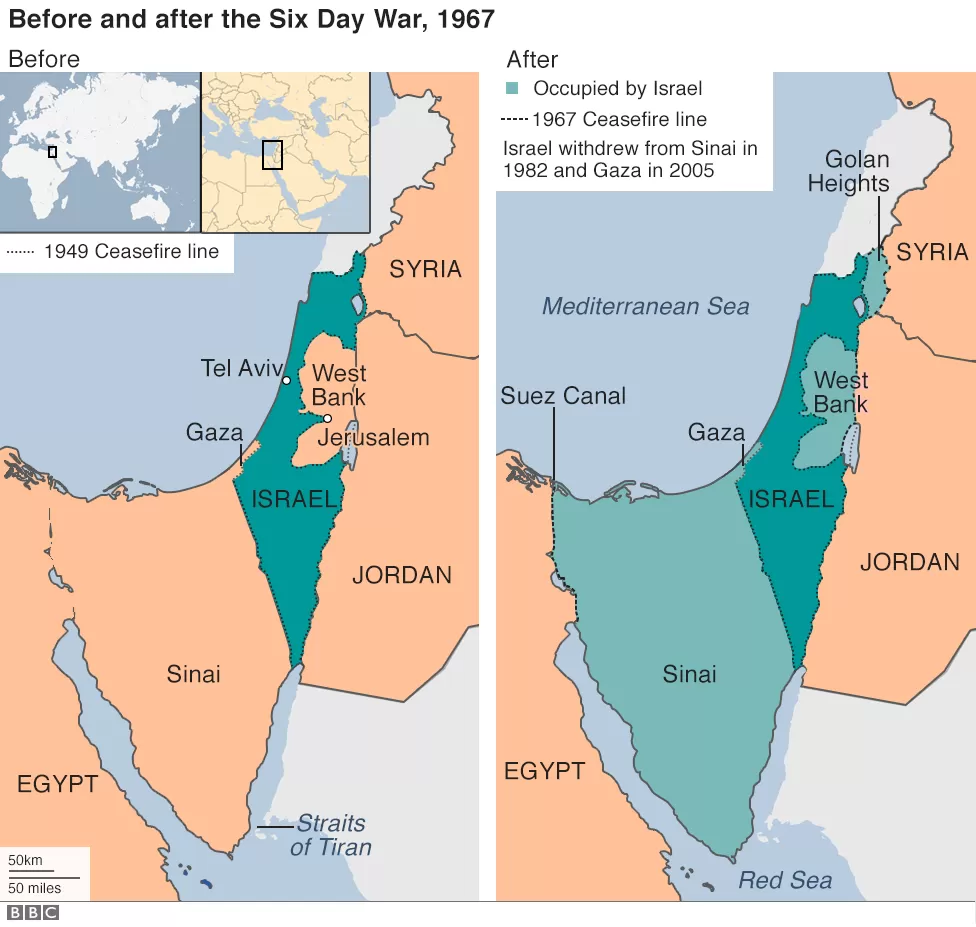
In October 1956, Egypt, Jordan and Syria formed a joint military command that alarmed Israel. When the USA and UK backed down on their decision to finance the development of an Aswan dam project for Egypt, President Nasser nationalised the Suez Canal, declaring that the transit fees would be used to pay for the infrastructure.
In retaliation, Britain and France orchestrated an attack on Egypt to reclaim the Suez. In the process, Israel was brought into the picture. On 29 October 1956, Israel invaded Sinai. On 5 November, the British and French deployed paratroopers along the Suez Canal. From October 1956 to March 1957, the Suez Canal was closed as a result of the crisis.
The [Suez] canal had been built during the 1860s under French management in partnership with Egypt. The canal itself was Egyptian, guaranteed as an open waterway under an international treaty, the Convention of Constantinople, signed in 1888. But the canal was operated by an unusual private firm, the Universal Suez Canal Company, headquartered in Paris. The British had bought a large minority of the stock from a bankrupt Egyptian government in 1875. The company had a concession to operate the canal until 1968. Surrounding the canal, loaded with infrastructure such as railroads, harbors, and warehouses, was the Canal Zone – an elaborate British base operated under an Anglo-Egyptian treaty signed in 1936.
An excerpt taken from “Suez Deconstructed: An Interactive Study in Crisis, War, and Peacemaking” by Philip Zelikow and Ernest May.
The First United Nations Emergency Force: UNEF I
On 7 November 1956, the United Nations General Assembly passed resolution 1001, leading to the creation of a peacekeeping force, known as the First United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF I). UNEF I was tasked to secure and supervise the cessation of hostilities, including the withdrawal of foreign troops (France, Britain and Israel) from Egyptian territory. Also, the UNEF I functioned as a buffer between Egyptian and Israeli forces, monitoring a ceasefire agreement that lasted for ten years.
Through the efforts of Canada’s Minister for External Affairs Lester Pearson and various European delegates, on February 2 the General Assembly passed two resolutions that focused on both Egypt and Israel. The first deplored Israeli noncompliance with the earlier General Assembly resolution that had mandated a complete Israeli withdrawal from all occupied territory and called upon Israel to complete its pullback without delay. The second resolution called upon both countries to observe the armistice agreement and, after Israeli troops withdrew, mandated the stationing of UNEF troops on the Israeli-Egyptian border.
An excerpt taken from “The Economic Diplomacy of the Suez Crisis” by Diane B. Kunz.
With the help of the charismatic Secretary-General Dag Hammarskjöld, Nasser agreed to the presence of UNEF I on the condition that Egypt could revoke its agreement at any time. Furthermore, the peacekeeping troops stationed in Egypt have no authority over the people. On the other hand, Israel refused to give UNEF consent to enter its territory.
By February 1957, UNEF I had 6073 personnel, which were contributed by eleven member states of the United Nations (Yugoslavia, Finland, India, Indonesia, Norway, Sweden, Canada, Brazil, Colombia, Denmark and Norway).
Six-Day War: A political bystander?
However, Egypt no longer welcomed UNEF’s presence by 1967. Given Israel’s participation in the invasion of Egypt during the Suez Canal Crisis as well as its hostility following the Palestinian War of 1948, tensions were high.
In May 1967, the Soviet Union delivered reports to Egypt, claiming that Israeli troops were amassing on the Syrian border. In anticipation of a possible military incursion, Nasser withdrew consent, forcing Secretary-General U Thant to comply with the expulsion of UNEF stationed in the Sinai Peninsula.
On 13 May 1967, [Nasser] received a Soviet intelligence report claiming that Israel was massing troops on Syria’s border. Nasser responded by taking three successive steps that made war virtually inevitable: he deployed his troops in the Sinai close to Israel’s border, he expelled the UN Emergency Force (UNEF) from the Sinai, and, on 22 May, he closed the Straits of Tiran to Israeli shipping. In Israeli eyes, this was a casus belli, a cause for war. On 5 June, Israel seized the initiative and launched the short, sharp war that ended in a resounding military defeat for Egypt, Syria, and Jordan.
An excerpt taken from “The 1967 Arab-Israeli War: Origins and Consequences” by Avi Shlaim and William Roger Louis.
Egypt then declared its intention to impose a blockade through the Straits of Tiran, which would have hampered Israel’s access to the Red Sea. Israel was outraged by this announcement, declaring the blockade as an act of war. On 5 June 1967, Israel commenced Operation Focus, which was a series of pre-emptive air strikes that disabled Egyptian air operations. This marked the start of the Six-Day War.
Evidently, the UN peacekeepers were helpless to the situation in spite of their initial success in response to the Suez Crisis.
What can we learn from this article?
Consider the following question:
– How far do you agree that the key factor that determined the successes of United Nations peacekeeping was the cooperation of member states?
Join our JC History Tuition to learn more about the United Nations. The H2 and H1 History Tuition feature online discussion and writing practices to enhance your knowledge application skills. Get useful study notes and clarify your doubts on the subject with the tutor. You can also follow our Telegram Channel to get useful updates.
We have other JC tuition classes, such as JC Math Tuition and JC Chemistry Tuition. For Secondary Tuition, we provide Secondary English Tuition, Secondary Math tuition, Secondary Chemistry Tuition, Social Studies Tuition, Geography, History Tuition and Secondary Economics Tuition. For Primary Tuition, we have Primary English, Math and Science Tuition. Call 9658 5789 to find out more.











