What is the Mischief Reef incident?
Topic of Study [For H2 History Students]:
Paper 2: Regional Conflicts and Co-operation
Source Based Case Study
Theme III Chapter 2: ASEAN (Growth and Development of ASEAN: Building regional peace and security – relations between ASEAN and external powers)
What is the ‘Mischief Reef’?
The Mischief Reef has many names: The Philippines calls it the Panganiban Reef, whereas China describes it as 美濟礁 (Meiji Reef) and the Vietnamese labels it as Đá Vành Khăn. It is a low-tide elevation located in the Spratly Islands in the South China Sea. Although the Mischief Reef is within the Philippines’ Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), which was established as within 200 nautical miles from the country as stated by 1982 UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS III), China has made claims to this disputed territory.
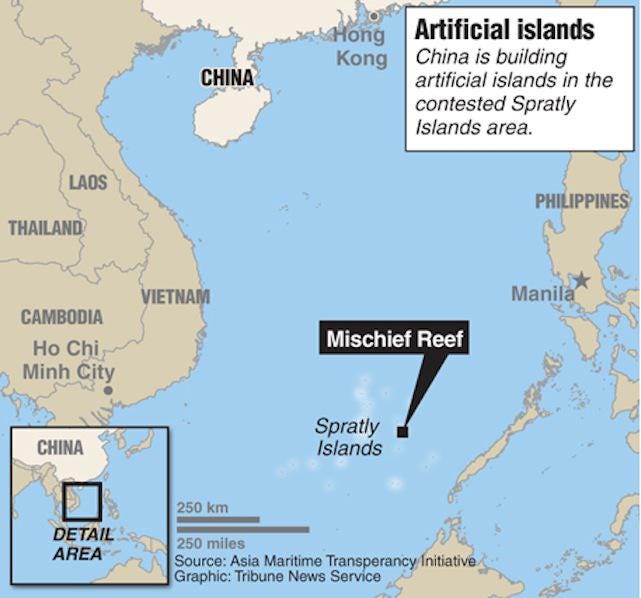
The dispute
On 8 February 1995, the Philippine authorities identified eight Chinese ships in the vicinity of the Philippine-claimed Mischief Reef. In April 1995, these authorities publicised the arrest of 62 Chinese fishermen in the hotly-contested area, charging them with the violation of international law. The situation deteriorated when the Philippines identified Chinese markers on the Mischief Reef and other islands.
In response, the Philippines declared its intention to built 7 lighthouses to assert Filipino claims and support international navigation. Additionally, the government internationalised the matter, hoping to garner support from its long-term ally, the USA, which was bounded by the 1951 Mutual Defense Treaty.
The 1995 China/Philippines incident involving Mischief Reef (Meijijiao/Panganiban) may have had its origins in September 1994, when the Philippine armed forces detained some 55 fishers from the People’s Republic of China who tried to set up homes on one of the islands claimed by the Philippines. They were charged with illegal entry and illegal possession of explosives. In what may have been a tit-for-tat, China detained 35 Filipino fishers for a week in late January 1995 in the area of the Spratlys which the Philippines claimed and calls Kalayaan. Then on February 8, 1995, the Philippines accused China of breaking international law by stationing armed vessels at, and building structures on, the feature it calls Panganiban (Mischief Reef).
An excerpt taken from “Sharing the Resources of the South China Sea” by Mark J. Valencia, Jon M. Van Dyke and Noel A. Ludwig.
Although China ratified the UNCLOS III in 1996, she provoked the Philippines and Vietnam by using a method of measurement to calculate her territorial waters. This method was applicable only to countries that are archipelagic, yet China was not classified as such.
ASEAN Response
On 18 March 1995, ASEAN Foreign Ministers issued a joint statement in view of the Mischief Reef incident, expressing concern over the regional stability in the South China Sea. Although the statement intentionally omitted any mention of China, it was clearly directed at this active claimant. As described by the former Thai diplomat Pavin Chachavalpongpun, ASEAN member nations raised the matter on the South China Sea dispute, hoping to engage China amicably.
At the first meeting of the ASEAN and Chinese senior Foreign Ministry officials, in April 1995 in Hangzhou, a forum that I had proposed the year before, the ASEAN delegations raised pointed questions about the Chinese position on the South China Sea and particularly about the developments on Mischief Reef.
[…] Nevertheless, the discussions were significant, being the first time that China dealt with the South China Sea question in a multilateral setting, as opposed to its preference for discussing it only bilaterally.
An excerpt taken from “Entering Uncharted Waters? ASEAN and the South China Sea” by Pavin Chachavalpongpun.
What can we learn from this article?
Consider the following question:
– How far do you agree that the South China Sea dispute was effectively managed by ASEAN?
Join our JC History Tuition to learn more about ASEAN and the South China Sea dispute. The H2 and H1 History Tuition feature online discussion and writing practices to enhance your knowledge application skills. Get useful study notes and clarify your doubts on the subject with the tutor. You can also follow our Telegram Channel to get useful updates.
We have other JC tuition classes, such as JC Math Tuition and JC Chemistry Tuition. For Secondary Tuition, we provide Secondary English Tuition, Secondary Math tuition, Secondary Chemistry Tuition, Social Studies Tuition, Geography, History Tuition and Secondary Economics Tuition. For Primary Tuition, we have Primary English, Math and Science Tuition. Call 9658 5789 to find out more.











